Organizational Framework
OPM’s divisions and offices and their employees implement the programs and deliver the services that enable the agency to meet its strategic goals and fulfill its statutory mandates. The agency’s organizational framework consists of offices that directly and indirectly support the agency’s mission.
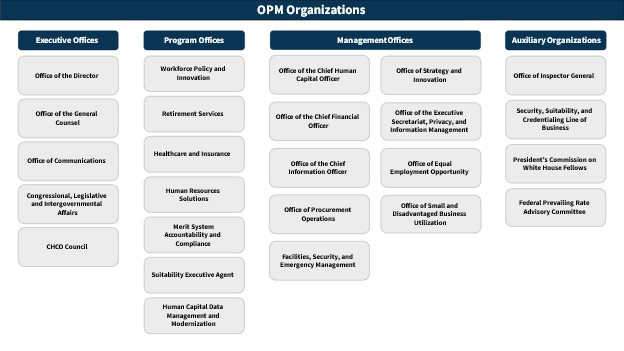
Organizational Chart Description
Executive Offices
Office of the Director (OD) provides guidance, leadership, and direction necessary to achieve OPM’s mission to lead and serve the Federal Government by delivering policies and services to achieve a trusted, effective civilian workforce.
Office of the General Counsel (OGC) ) provides legal advice and representation to the Director and OPM managers and leaders. OGC does this by rendering opinions, reviewing proposed policies and other work products, commenting on their legal efficacy, serving as agency representatives in administrative litigation, and supporting the Department of Justice in its representation of the Government on matters concerning the civilian workforce. OGC also carries out several programmatic, substantive functions that fulfill other statutory or regulatory mandates and, thus, benefit other OPM offices or the Executive Branch as a whole. For example, OGC is responsible for promulgating Hatch Act regulations, administers the internal agency Hatch Act and ethics programs, and serves in a policy and legal role in the Government-wide function of determining which Merit Systems Protection Board and arbitral decisions are erroneous and have a substantial impact on civil service law, and, thus, merit judicial review. Consistent with the Government in Ethics Act, OGC, along with the Department of Justice, consults with the United States Office of Government Ethics on any regulations related to the Standards of Conduct the Office of Government Ethics plans to issue. OGC also administers OPM’s internal program for handling claims lodged under the Federal Tort Claims Act and other statutes and determines when OPM personnel or documents should be made available in discovery to parties in litigation to which OPM is not a party.
Office of Communications (OC) coordinates a comprehensive effort to inform the public of the Administration’s and OPM’s goals, plans, and activities through various media outlets. The OC provides the American public, Federal agencies, and pertinent stakeholders with accurate information to aid in planning and decision-making. The OC supports enterprise-wide digital transformation initiatives and oversees the development of all video products, printed materials, and web content generated by OPM offices. The office develops briefing materials for the Director and other OPM officials for various activities and events. The OC also plans events that amplify the Administration’s and OPM’s agency and Government-wide initiatives.
Congressional, Legislative and Intergovernmental Affairs (CLIA) is the OPM office that fosters and maintains relationships with Members of Congress and their staff. CLIA accomplishes its mission by keeping informed of issues related to programs and policies administered by OPM. CLIA staff attend meetings, briefings, markups, and hearings to interact, educate, and advise agency leadership and the Congress. CLIA is also responsible for supporting congressional efforts by providing technical assistance and substantive responses to congressional inquiries. Additionally, CLIA is responsible for working with OPM program offices to successfully respond to Congressional casework inquiries.
Chief Human Capital Officers Council (CHCOC) serves as the principal interagency forum to advise and coordinate the activities of the agencies of its members on various matters. The Council is structured with a Chair, a Vice Chair, an Executive Director, a Deputy Director, 26 CHCOs, 26 Deputy CHCOs, the Small Agencies Human Resources Council (SAHRC) chair, and the SAHRC vice chair. The OPM Director serves as the Chair of the Council and attends the Council’s monthly meetings, speaking each time to the work of OPM as an agency and providing opportunities for CHCOs to weigh in as strategic partners to the agency. The OPM Director serves as the final decision maker for Council activities. The Deputy Director for Management at the Office of Management and Budget serves as the Vice Chair of the Council attending monthly meetings. The Council informs and coordinates the activities of its member agencies on such matters as modernization of human resources systems and practices and improving quality of human resources data and information. At the request of the Chair, the Council may provide views to Office of Personnel Management (OPM), the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), and agency leaders on human capital strategies and policies, as well as on the assessment of human capital management in Federal agencies. The Council identifies and shares promising practices with CHCOs and other officials with similar responsibilities in fulfilling their individual responsibilities in an effort to: promote a culture of continuous human capital learning and high performance; embrace strategies, policies, and processes to develop and support a modernized federal workforce and workplace; support consistency in the implementation of the laws governing the Federal civil service; and support agency leaders in carrying out their responsibilities for selecting, developing, training, and managing a diverse, inclusive, high-quality, productive workforce in accordance with merit system principles.
Office of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion & Accessibility (ODEIA) is committed to leading and providing Government-wide guidance on DEIA initiatives, including technical assistance to agencies, policy guidance, management of intergovernmental working groups on DEIA, and the Government-wide DEIA Strategic Plan. ODEIA provides Federal agencies with concrete strategies and leading practices to recruit, hire, include, develop, retain, engage, and motivate a diverse, high-performing workforce. ODEIA primarily focuses its actions on externally facing customers and matters, but it also has an advisory function to senior leaders for internal OPM DEIA efforts.
Program Offices
Workforce Policy and Innovation (WPI) is OPM’s Government-wide workforce policy office. Formerly known as Employee Services (ES), WPI administers statutory and regulatory provisions related to recruitment, hiring, classification, strategic workforce planning, pay, leave, performance management and recognition, leadership and employee development, training, reskilling, work/life/wellness programs, labor and employee relations, and management and oversight of Federal Executive Boards. WPI equips Federal agencies with tools, flexibilities, and authorities, as well as forward-leaning strategic workforce planning products, to enable agencies to hire, develop, and retain an effective Federal workforce.
Retirement Services (RS) is responsible for the administration of the Federal Retirement Program covering approximately 2.8 million active employees, including the United States Postal Service, and more than 2.7 million annuitants, survivors, and family members. RS develops and administers benefits programs and services that offer value and quality to help maintain the Government’s position as a competitive employer. Activities include maintaining records and servicing credit accounts prior to retirement; initial eligibility determinations at retirement; adjudication of annuity benefits based on age and service, disability, or death according to relevant statutes and regulations. Once a case is adjudicated and added to the annuity roll, OPM continues to serve annuitants by making address or tax status changes to annuitant accounts, sending annual cost of living and tax information, surveying certain annuitants to confirm their continued eligibility to receive benefits, and conducting other post-adjudication activities.
Healthcare and Insurance (HI) consolidates OPM’s health and other insurance benefits responsibilities into a single organization. This includes contracting, contract oversight, program development, and management functions for the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) Program, the Postal Service Health Benefits (PSHB) Program, the Federal Employees’ Group Life Insurance Program, the Federal Long-Term Care Insurance Program, the Federal Employees Dental and Vision Insurance Program, and the Federal Flexible Spending Account Program. HI consists of Program Development and Support, Federal Employee Insurance Operations, Postal Service Insurance Operations, Office of the Actuaries and Operations, Resource Management divisions, and front office staff, including the Chief Pharmacy Officer and the Chief Medical Officer.
Program Development and Support is responsible for extensive operational, analytical, and systems development and support; program policy and development and implementation; data collection and analysis; and stakeholder outreach and education for programs administered by HI. Program Development and Support also manages the annual Federal Benefits Open Season and outreach, education and collaboration with agency benefits officers.
Federal Employees Insurance Operations (FEIO) is responsible for the contracting operations for all insurance programs, the Plan Performance Assessment function connecting health plan quality to carrier profit, the Audit Resolution & Compliance function facilitating and tracking audit responses and resolution, and the Contract Administration and Program Support responsible for leading projects important to insurance operations, including carrier brochure changes and contract amendments. Postal Service Insurance Operations will perform similar functions to FEIO for the new Postal Service Health Benefits Program.
The Office of the Actuaries reviews premium proposals from FEHB and Federal Employees Dental Vision Insurance Plan carriers, determines the actuarial liabilities, contributions, and funding payments for the Retirement, Health and Life Insurance programs, and provides actuarial support for employee benefit programs including the FEHB Program, Federal Employees’ Group Life Insurance, Federal Long-Term Care Insurance Program, Federal Employees Dental and Vision Insurance Program, Civil Service Retirement System, Federal Employees Retirement System, and the Federal Flexible Spending Account Program.
Human Resources Solutions (HRS) provides human capital products and services that support Federal agencies in meeting their mission. Through both internal human capital experts and/or private sector partners, HRS helps agencies recruit and hire top talent, cultivate leaders, build Federal human resources capacity, optimize the performance management process, and sustain effective results-oriented organizations. HRS operates under the provisions of the Revolving Fund, 5 U.S.C. §1304 (e)(1), that authorizes OPM to perform personnel management services for Federal agencies on a cost reimbursable basis. HRS consists of four practice areas that work directly with customer agency partners via Interagency Agreement to deliver a complete range of human resources products and services, including government-to-government and private sector solutions. Some of this work is directed by statute, and other aspects are performed at the option of an agency that engages HRS in this work. This includes recruiting and examining candidates for positions for employment by Federal agencies nationwide; delivering leadership and development courses and programs, including the Leadership for a Democratic Society program; providing custom-designed technology systems (e.g., USAJOBS, USA Staffing, USA Hire℠, USA Performance®, and USALearning) to support Federal agency recruitment, talent acquisition, performance management, and training priorities; developing organization and performance management strategies; and providing human capital management, organizational performance improvement, and training and development expertise delivered through best-in-class contracts.
Merit System Accountability & Compliance (MSAC) is responsible for a range of functions that support OPM’s mission as a Federal human capital leader and its stewardship of the merit system. MSAC evaluates agencies’ HR operations and human capital management programs for efficiency and effectiveness. It provides guidance as a trusted human capital partner of Federal agencies to help align their practices with merit system principles and other civil service requirements. MSAC also conducts special cross-cutting studies to assess the use of HR authorities and flexibilities across the Government. Moreover, MSAC reviews and renders decisions on agencies’ requests to appoint current or former political appointees to positions in the competitive service, the non-political excepted service, or the senior executive service to verify that such appointments conform to applicable selection requirements and are free of political influence. MSAC also adjudicates classification appeals, job grading appeals, Fair Labor Standards Act claims, compensation and leave claims, and declination of reasonable offer appeals, all of which provide Federal employees with administrative procedural rights to challenge compensation and related agency decisions without having to seek redress in Federal courts. MSAC has Government-wide oversight of the Combined Federal Campaign and the Voting Rights programs. The mission of the Combined Federal Campaign is to promote and support philanthropy through a program that is employee focused, cost-efficient, and effective in providing all Federal employees and annuitants the opportunity to improve the quality of life for all. The Voting Rights Program deploys Federal observers to monitor polling sites (as determined by the Attorney General) and provides written reports to the Department of Justice. Further, MSAC serves as the liaison between OPM program offices and oversight groups such as the Office of the Inspector General and the Government Accountability Office (GAO) and helps to coordinate audit activities to resolve recommendations.
Suitability Executive Agent (SuitEA) was established as a distinct program office within OPM in December 2016 to strengthen processes for personnel vetting, suitability determinations for Federal employment and Government contract work, and personnel credentialing for access to agency systems and facilities across the Government. SuitEA prescribes suitability, fitness, and credentialing standards and procedures and oversees functions delegated to the heads of agencies while retaining jurisdiction for certain suitability determinations and taking Government-wide suitability actions when appropriate. It also issues guidelines and instructions to the heads of agencies to promote appropriate uniformity, centralization, efficiency, effectiveness, reciprocity, timeliness, and security in suitability/fitness/credentialing processes, and delivers training to suitability and fitness adjudicators across Government.
Human Capital Data Management and Modernization (HCDMM) leads the Government-wide use of human capital data as a strategic asset through innovations in human capital service delivery models, interoperable data management, and decision-support analytics and tools.
HCDMM establishes human capital data standards and manages data collection processes including the Federal guides for working with and managing human capital data, requirements for data file submissions to OPM, protocols for human capital data releases, statistical analyses, data science, product development, and delivery of analytical tools and services.
HCDMM includes the Human Resource Quality Services Management Office, which is establishing a marketplace of services and products that enables agencies to improve the delivery of human capital activities in alignment with OPM’s human capital data standards.
Management Offices
Office of the Chief Human Capital Officer is responsible for OPM’s internal human resources management programs. OPM HR supports the human capital needs of program offices throughout the employment lifecycle, from recruiting and hiring candidates for employment opportunities at OPM, to coordinating career development opportunities, to processing retirement applications. The OPM Chief Human Capital Officer (CHCO) leads HR and is responsible for shaping corporate human resources strategy, policy, and solutions to workforce management challenges within the agency.
Office of the Chief Financial Officer (OCFO) is responsible for OPM’s strategic financial management, fiscal responsibility, transparency, and accountability. OCFO advises the OPM Director and senior leadership on all aspects of financial management and delivers services to OPM customers, enabling OPM to achieve its strategic plan objectives and deliver on its mission. OCFO facilitates financial planning, budgeting, and accounting functions, ensuring adherence to financial regulations and compliance standards. OCFO also manages the agency’s financial systems, and performs internal control reviews. OCFO aligns financial decisions with the agency’s goals and decision-making processes, optimizing resource allocations and showcasing the effective management of taxpayer dollars. OCFO strives for excellence in strategic financial management, leading OPM with the practice of sound financial management in program development and operations and the stewardship of public resources.
Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) defines the enterprise information technology (IT) vision, strategy, policies, and cybersecurity for OPM. The OCIO determines the most effective use of technology to support of the agency’s strategic plan, including the enterprise architecture, platform, systems, and applications. The OCIO is responsible for modernizing information technology, developing and maintaining the agency’s information technology security policies, and operating and enhancing the agency’s cybersecurity program. The OCIO evaluates and leverages emerging technology including Artificial Intelligence capabilities to improve business operations. The OCIO leads the IT governance processes and IT investment management to develop IT strategies and budgets across the agency. The OCIO provides technical strategies and guidance, cloud technology and services, application and system development and maintenance, IT project management, agile frameworks, collaboration and communication tools, hardware, software, and infrastructure such as the OPM Help Desk services to support OPM’s business operations. The OCIO manages pre- and post-implementation reviews of information technology programs and projects. The OCIO reviews and oversees IT acquisitions, services, and spending. Further, the OCIO partners with other agencies on Government-wide initiatives such as IT modernization, the optimization of enterprise services, and the development of long-term plans for human resource IT strategies.
Office of Procurement Operations (OPO) awards and administers contracts and interagency agreements. OPO provides acquisition services to OPM’s programs and provides assisted acquisition services for other Federal agencies that require support under OPM contracts. OPO is responsible for the agency suspension and debarment program and supports OPM’s small business utilization efforts in accordance with law and OPM contracting policies. The Acquisition Policy and Innovation function within OPO provides acquisition policy development and guidance agency-wide, as well as compliance and oversight for OPM’s procurement program. OPO provides acquisition support and oversight for all Contracting Officers and Contracting Officer’s Representatives and manages and oversees the agency purchase card program. OPO serves as OPM’s liaison to the Office of Federal Procurement Policy, Chief Acquisition Officers Council, and other key external agency partnerships.
Office of Strategy and Innovation (OSI) provides OPM with the evidence, resources, and support necessary to make better-informed policy and budgeting decisions, improve organizational performance, foster transparency in how the agency is performing, promote accountability for delivering results to the agency’s customers, and enable a culture of continuous learning by leading the agency’s strategic planning, organizational performance management, process improvement, customer experience improvement, research and evaluation, program and project management improvement, and enterprise risk management functions. OSI implements key management requirements for OPM: the Government Performance and Results Modernization Act of 2010, the Program Management Improvement Accountability Act of 2016, evaluation functions of the Foundations for Evidence-Based Policymaking Act of 2018, OMB Circular A-11 Part 6: The Federal Performance Framework for Improving Program and Service Delivery, and the enterprise risk management functions of OMB Circular A–123, Management’s Responsibility for Enterprise Risk Management and Internal Control.
Facilities, Security and Emergency Management (FSEM) manages the agency’s real property, building operations, space design and layout, mail management, physical security and safety, and occupational health programs. FSEM provides personnel security, suitability, and national security adjudicative determinations for OPM personnel. FSEM oversees OPM’s Personal Identification Verification program and provides shared services in support of other Government agencies’ adjudicative programs. FSEM directs the operations and oversees OPM’s classified information, industrial security, insider threat, and preparedness and emergency response programs. In addition, it oversees publishing and printing management for internal and external design and reproduction, as well as the agency’s mail center operations.
Office of the Executive Secretariat, Privacy, and Information Management (OESPIM) is responsible for privacy, Freedom of Information Act, records management, forms management/Paperwork Reduction Act, Controlled Unclassified Information, correspondence management, coordination of OPM’s internal clearance processes (to include policy and program proposals), and regulatory affairs (to include serving as the agency’s liaison with the Office of Management and Budget and the Federal Register).
Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) provides a fair, legally correct, and expeditious Equal Employment Opportunity complaints process, including Equal Employment Opportunity counseling, Alternative Dispute Resolution, and Equal Employment Opportunity Complaints Intake, Investigation, Adjudication, and Record-Keeping.
Office of Small and Disadvantaged Business Utilization (OSDBU) is authorized by the Small Business Act (Act) to oversee OPM’s compliance with the achievement of annual small business goals. The Office of Small and Disadvantaged Business Utilization manages the development and implementation of appropriate outreach programs aimed at heightening the awareness of the small business community to the contracting opportunities available within OPM. The Act also directs the Office of Small and Disadvantaged Business Utilization to manage its in-reach and outreach activities under three lines of business: advocacy, outreach, and unification of the business process.
Auxiliary Organizations
Office of the Inspector General (OIG) is the independent office that conducts comprehensive audits, investigations, and evaluations relating to OPM programs and operations. It is responsible for administrative actions against health care providers that commit sanctionable offenses with respect to the FEHB Program or other OPM programs. The Office of the Inspector General keeps the Director and Congress fully informed about problems and deficiencies in the administration of agency programs and operations, and the need for and progress of corrective action.
President’s Commission on White House Fellows was founded in 1964 and is one of America’s most prestigious programs for leadership and public service. White House Fellowships offer exceptional young professionals firsthand experience working at the highest levels of the Federal Government. Selected individuals typically spend one year working as a full-time, paid Fellow to senior White House staff, Cabinet Secretaries, and other top-ranking Government officials. Fellows also participate in an education program consisting of roundtable discussions with renowned leaders from the private and public sectors. Fellowships are awarded on a strictly nonpartisan basis.
Federal Prevailing Rate Advisory Committee (FRAC) studies the prevailing rate system and other matters pertinent to the establishment of prevailing rates under Subchapter IV of Chapter 53 of Title V, United States Code, and advises the Director of OPM on the Government-wide administration of the pay system for blue-collar Federal employees.
Security, Suitability, and Credentialing Line of Business (SSLOB) is an interagency organization that is administratively housed within OPM. The Security, Suitability, and Credentialing Line of Business supports the Security, Suitability, and Credentialing Performance Accountability Council, including the Suitability and Credentialing and Security Executive Agents (the Director of OPM and the Director of National Intelligence). OMB’s Deputy Director for Management chairs the Council and is accountable to the President for promoting the alignment of personnel vetting processes and driving enterprise-wide reforms. The Security, Suitability, and Credentialing Line of Business assists the Council and the Executive Agents – through the Council’s Program Management Office – in its personnel vetting mission by identifying/implementing investments, simplifying the delivery of services, and establishing shared services, as well as promoting reciprocity, efficiency, and effectiveness across the enterprise.
OPM Organizations Chart Description
OPM Organizations divided into four categories: Executive Offices, Program Offices, Management Offices, and Auxiliary Organizations.
- Executive Offices
- Office of the Director
- Office of the General Counsel
- Office of Communications
- Congressional, Legislative, and Intergovernmental Affairs
- CHCO Council
- Program Offices
- Workforce Policy and Innovation
- Retirement Services
- Healthcare and Insurance
- Human Resources Solutions
- Merit Systems Accountability and Compliance
- Suitability Executive Agent
- Human Capital Data Management and Modernization
- Management Offices
- Office of the Chief Human Capital Officer
- Office of Strategy and Innovation
- Office of the Chief Financial Officer
- Office of the Executive Secretariat, Privacy, and Information Management
- Office of the Chief Information Officer
- Office of Equal Employment Opportunity
- Office of Procurement Operations
- Office of Small and Disadvantaged Business Utilization
- Facilities, Security, and Emergency Management
- Auxiliary Organizations
- Office of Inspector General
- Security, Suitability, and Credentialing Line of Business
- President’s Commission on White House Fellows
- Federal Prevailing Rate Advisory Committee